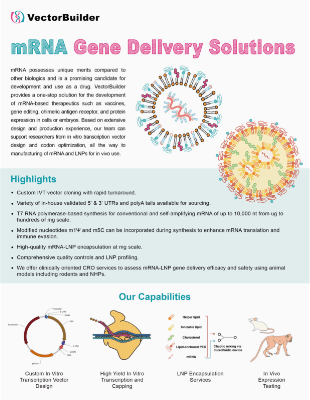
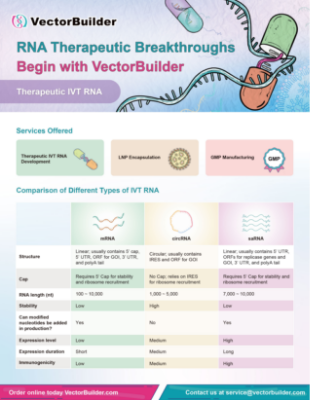
LNP Encapsulation
VectorBuilder offers lipid nanoparticle (LNP) encapsulation for RNA and plasmid delivery. Our service excels in producing homogeneous LNPs with a high encapsulation efficiency. Additionally, we can help our customers enhance their drug delivery efficiency and target tissues by conjugating tissue-targeting antibodies to LNPs or optimizing the LNP formulations. For large-scale manufacturing of LNP-RNA therapeutics, check out our CDMO services.
Talk to Our Experts
Highlights
- Standard (e.g. SM102, ALC-0315, MC3) and custom formulations available
- Can encapsulate various types of RNA/DNA molecules, including mRNA, saRNA, siRNA, Cas9 mRNA/sgRNA mix, circRNA, pDNA, etc.
- High encapsulation efficiency (up to 100%)
- Low (<0.1) polydispersity index (PDI)
- Antibody-conjugated LNPs available


IVT Vector
Design & Cloning
Design & Cloning
IVT RNA Production
LNP Encapsulation
Quality Control (QC)
Functional Validation
Please visit our Therapeutic IVT RNA Development page for more details or try our Premade LNP-RNA products.
Quality Control (QC)
VectorBuilder offers comprehensive QC for LNP encapsulated RNA and plasmids.
| Attribute | QC assay | Research-grade | GMP-like |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Visual inspection | √ | √ |
| Concentration | RiboGreen assay | √ | √ |
| Encapsulation efficiency | RiboGreen assay | √ | √ |
| Particle size | Dynamic light scattering (Zetasizer) | √ | √ |
| Polydispersity index (PDI) | Dynamic light scattering (Zetasizer) | √ | √ |
| Surface charge (Zeta potential) | Dynamic light scattering (Zetasizer) | √ | √ |
| Encapsulated RNA integrity | Capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE) | Optional | √ |
| Endotoxin | Kinetic chromogenic assay (KCA) | Optional | √ |
| pH | pH paper | Optional | √ |
| Sterility | Bioburden test | Optional | √ |
LNP-mRNA QC data
- TEM
- PDI and zeta potential
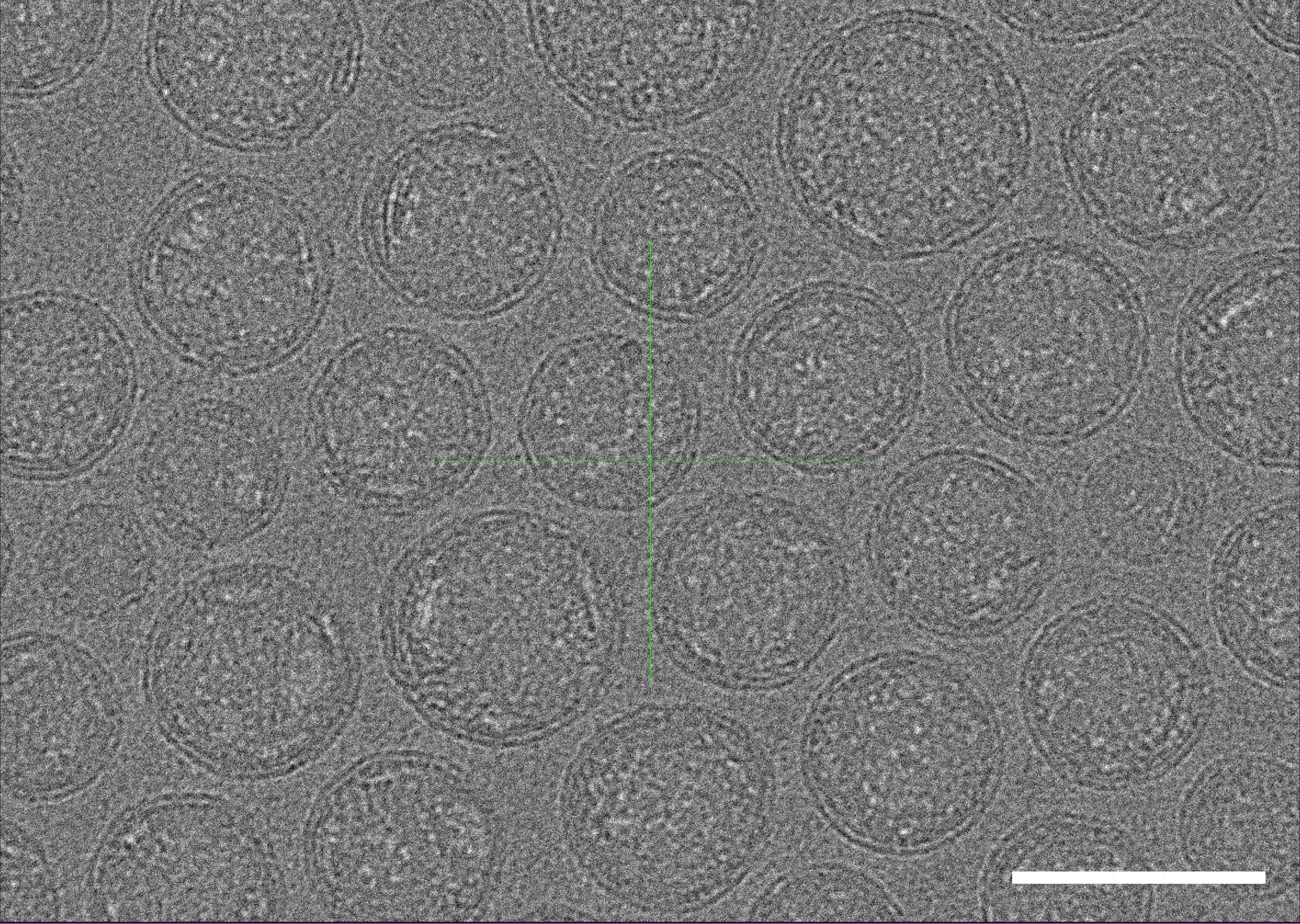
Figure 1. Cryo-TEM micrographs of LNP-mRNA. Scale bar=100 nm.
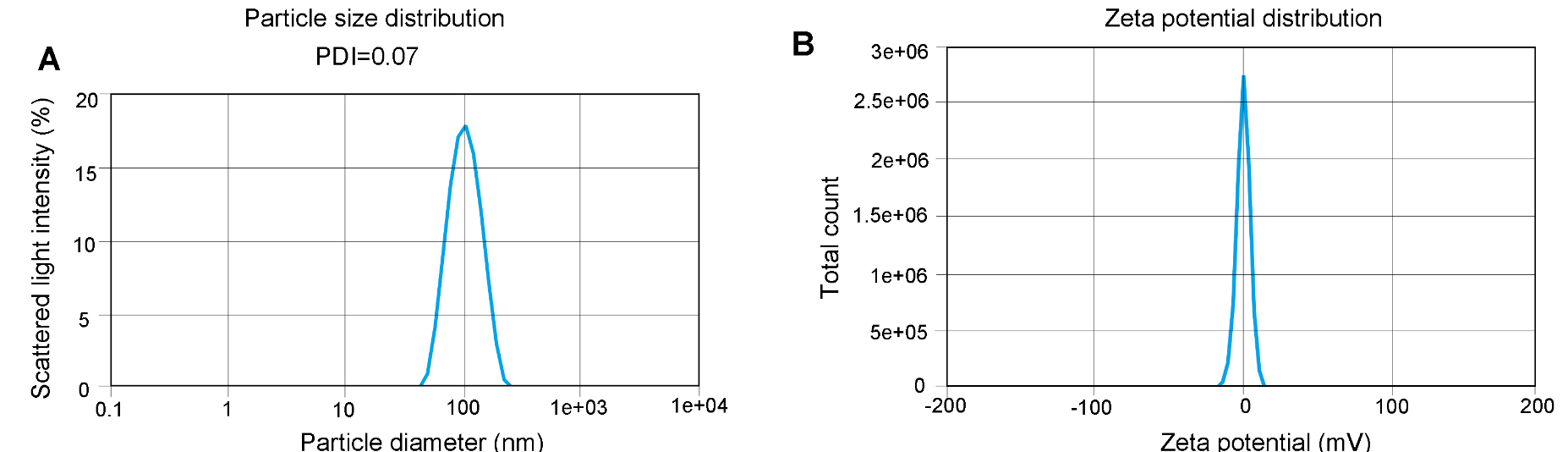
Figure 2. Particle size and Zeta potential distribution analysis. PDI (A) and Zeta potential (B) were determined by DLS which measures the intensity differences of fluctuated light due to motion of particles. Data demonstrates homogeneous LNP mixtures.
LNP-RNA functional validation
- LNP-mRNA expression in vitro
- LNP-mRNA expression in vivo
- Primary T cell LNP transfection
- Antibody-conjugated LNP
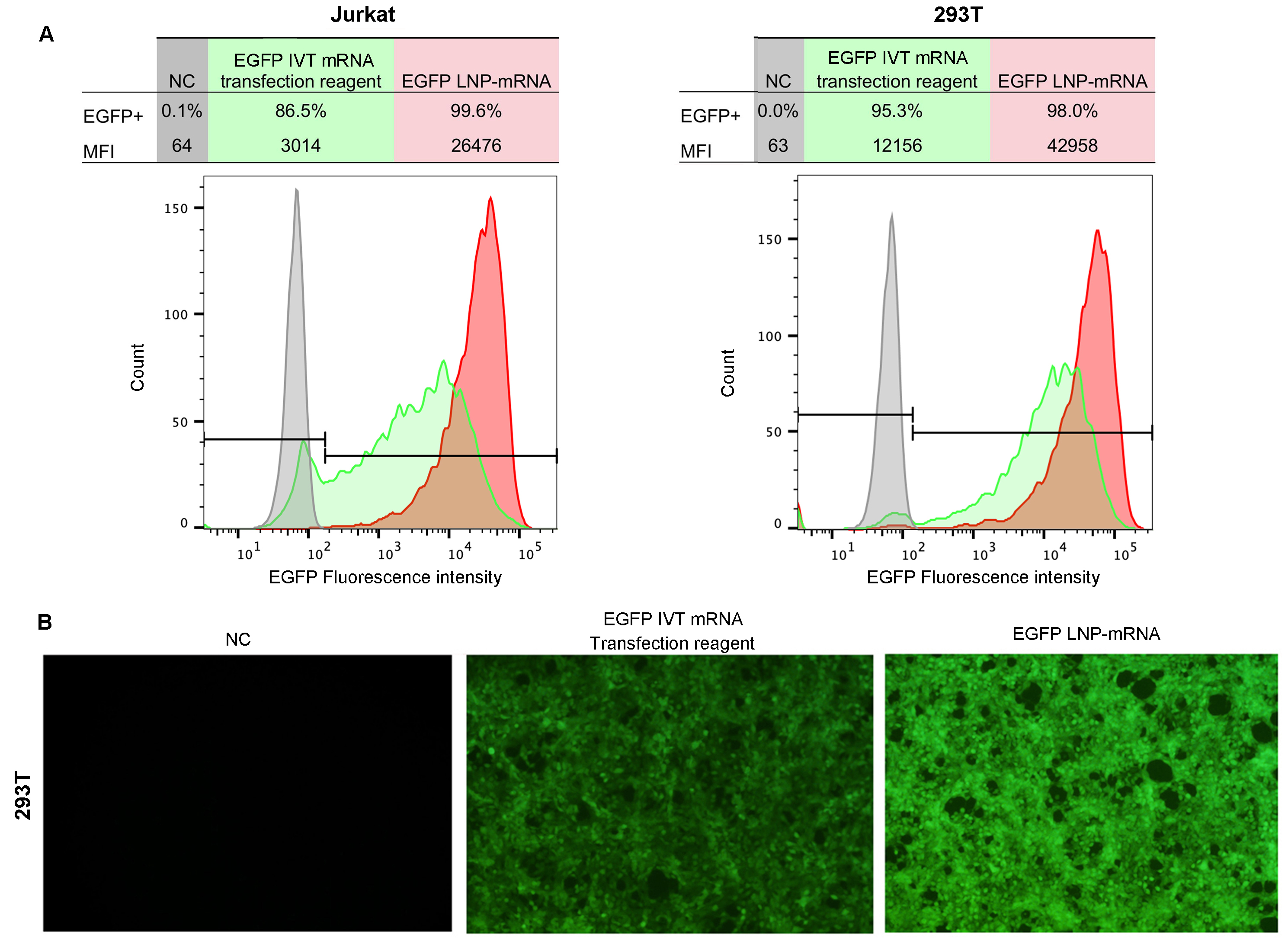
Figure 3. Efficient mRNA delivery and expression using LNP in vitro. Cells were transfected with LNP encapsulated EGFP mRNA or EGFP mRNA mixed with commercial transfection reagent. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of EGFP expression in Jurkat and HEK293T cells and (B) Fluorescent imaging of HEK293T cells at 24 hours post-transfection. MFI: median fluorescence intensity.
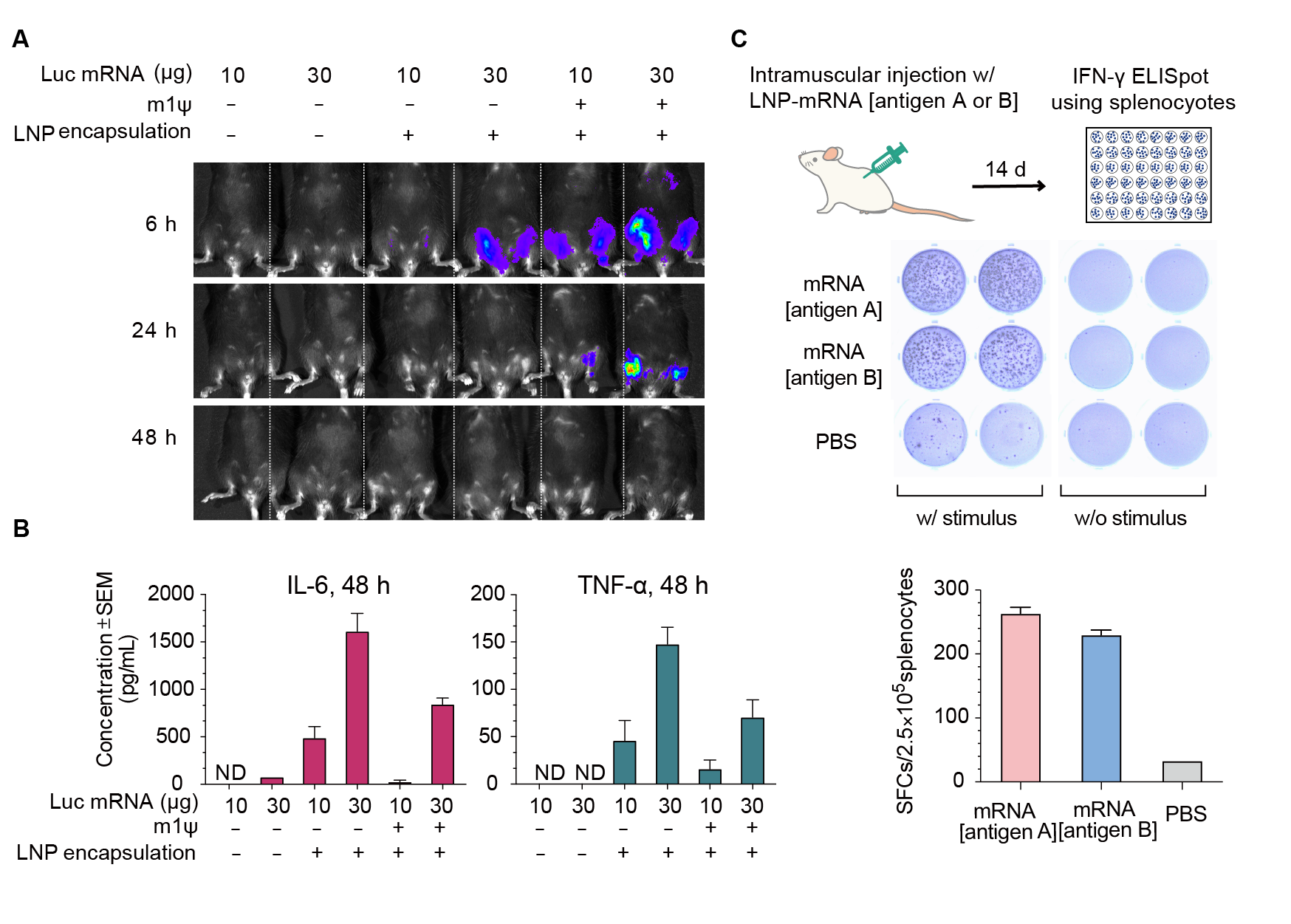
Figure 4. Expression of luciferase (Luc) mRNA and mRNA induced immune response in mice. (A) Luciferase activity visualized by live imaging at 6 h, 24 h, and 48 h post-injection. (B) Two pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-6 and TNF-⍺, were quantified in the serum at 48 h post-injection. Error bars represent standard errors. Mice strain: C57BL/6J; mice age: 8 weeks; injection method: intramuscular injection. (C) IFN-γ ELISpot assay of splenocytes derived from Balb/C mice 14 days post intramuscular injection of 30 ug LNP-encapsulated mRNA coding for viral antigen A, viral antigen B, or control PBS.
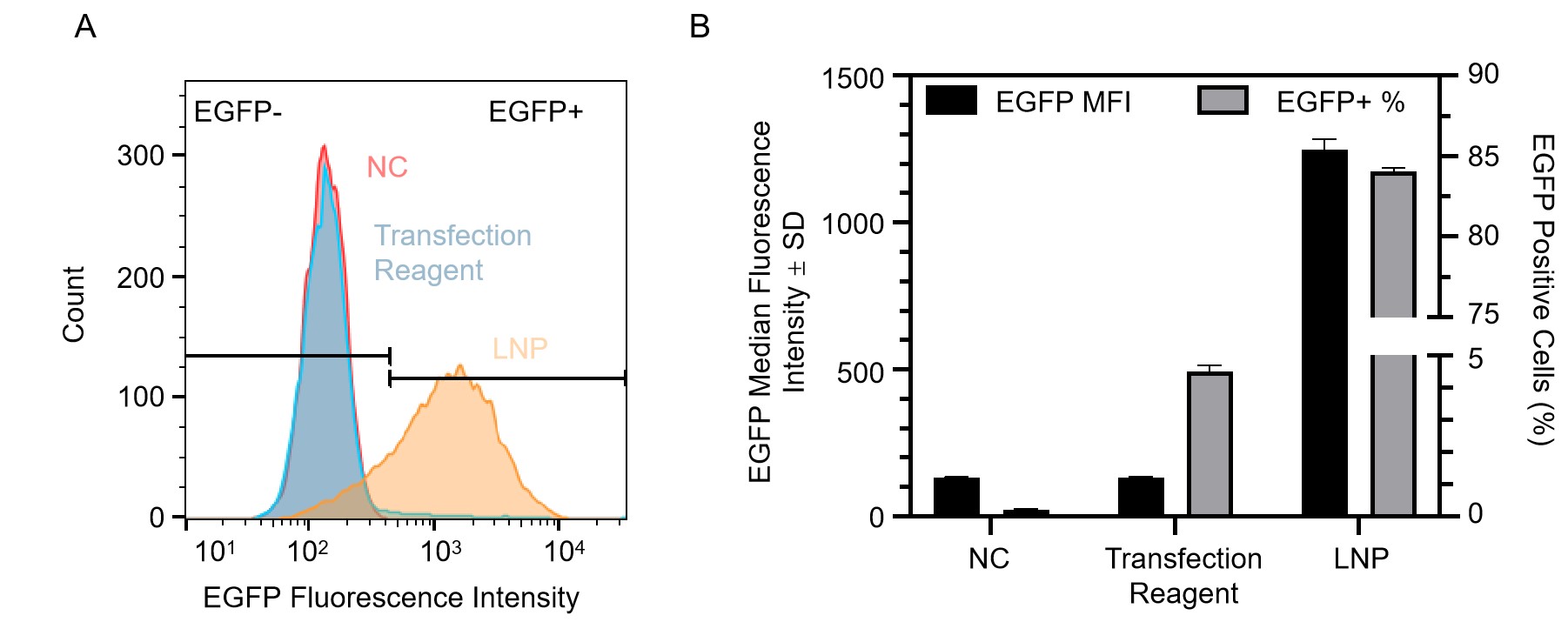
Figure 5. Transfection of primary T cells with EGFP mRNA. (A) Histogram count of cells expressing EGFP as measured by flow cytometry 24 hours after transfection. Primary T cells were subjected to three different treatments: no treatment control (NC), mRNA encapsulated with a commercial transfection reagent, and lipid nanoparticle encapsulated mRNA (LNP). (B) Corresponding quantification of median fluorescence intensity (MFI) (black) and the % of EGFP-positive cells (grey) as measured by flow cytometry.
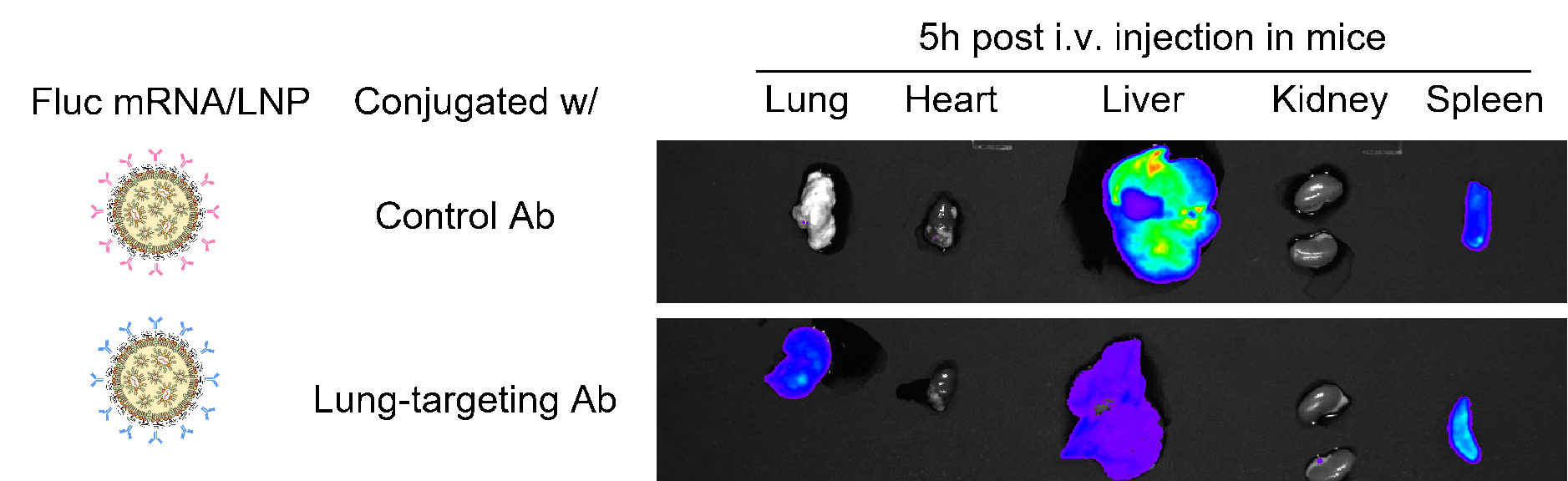
Figure 6. Anti-CD31 conjugated firefly luciferase (FLuc) LNP-mRNA showed improved luciferase expression in lung. Mice strain: C57BL/6J; mice age: 6-8 weeks; mice gender: female; administration route: tail vein. Negative controls: IgG2a-conjugated FLuc LNP-mRNA and naked FLuc mRNA.
Documents
Brochures & Flyers User InstructionsCertificate of Analysis (COA)
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)