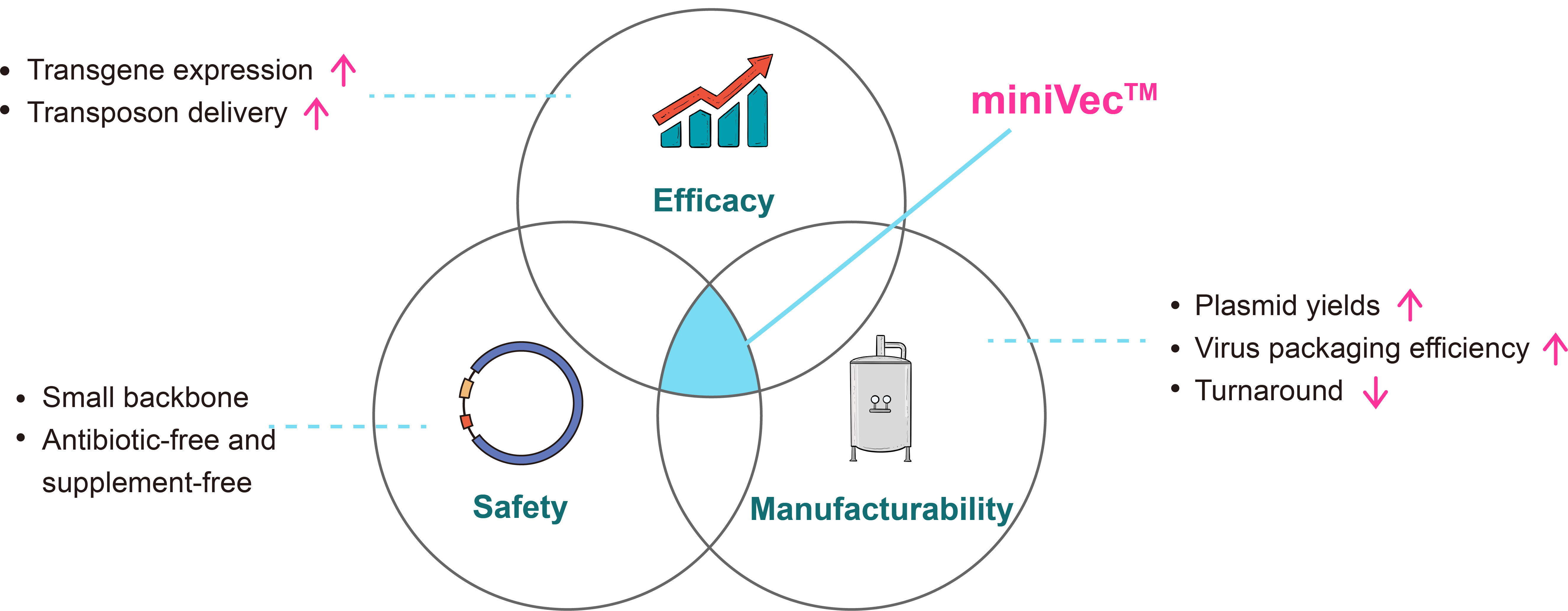
miniVec™ Plasmid

VectorBuilder's proprietary miniVec™ plasmid offers a miniaturized backbone, providing remarkable efficacy, safety, and manufacturability for cell and gene therapies. Comparing to traditional plasmids, miniVec™ plasmids have higher plasmid manufacturing and virus packaging yields, improved transgene expression, and an enhanced safety profile. The miniVec™ backbone supports antibiotic-free and supplement-free selection. miniVec™ plasmids can be applied across diverse expression systems, including lentivirus, AAV, in vitro transcription (IVT), non-viral regular plasmids, piggyBac, and Sleeping Beauty.
miniVec™ Technology
Figure 1 below depicts how the miniVec™ system works. As a key component of the system, miniHost™ is an engineered E. coli strain containing a growth inhibitor gene. After transforming with the miniVec™ plasmid, miniHost™ cells can be cultured in regular LB medium without the need for antibiotic-based selection. The VecSeqB transcribed from the miniVec™ backbone can block the growth inhibitor gene translation through RNA-RNA complementation with the VecSeqA which is positioned upstream of the growth inhibitor transcript. As a result, only the successfully transformed host cells proliferate robustly to produce high copies of the miniVec™ plasmids.
Such antibiotic-free selection offers multiple benefits, including enhanced safety and the ability to manufacture drug products without antibiotics. VectorBuilder's miniVec™ technology further distinguishes itself with its supplement-free cell survival mechanism, eliminating the need for additional supplements in LB media during vector production.
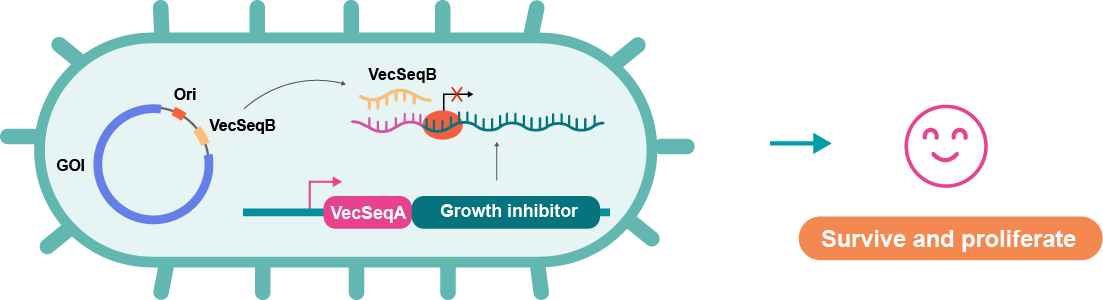
Figure 1. Mechanism of selection with miniVec™ backbone
Increased Plasmid Yields
miniVec™ plasmids can achieve higher manufacturing yields compared to traditional plasmids due to several key mechanisms including a high-copy-number favored fermentation, more efficient replication, and a reduced metabolic burden.
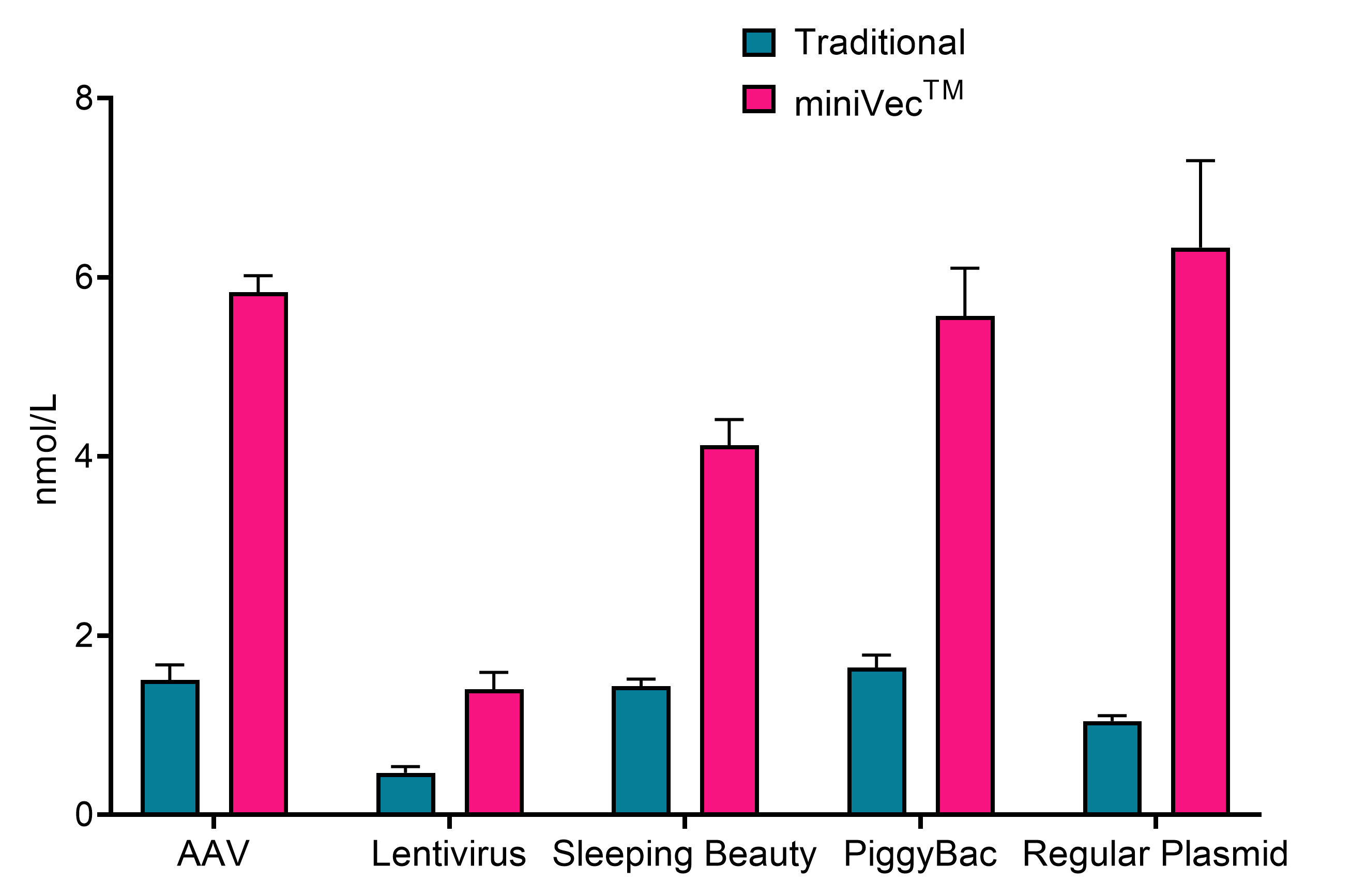
Figure 2. miniVec™ exhibits increased plasmid yields compared to traditional plasmids. Measurement of plasmid yields from lab-scale fermentation of E. coli cultures under the same conditions transformed with traditional or miniVecTM plasmids from different expression systems.
Enhanced Transgene Expression
miniVec™ plasmids have been validated for enhanced transgene expression in vitro compared to traditional plasmids. The minimal bacterial backbone, which mitigates the risk of an immune response in mammalian cells, can additionally minimize host cellular stress and exhibit increased cellular uptake and trafficking.
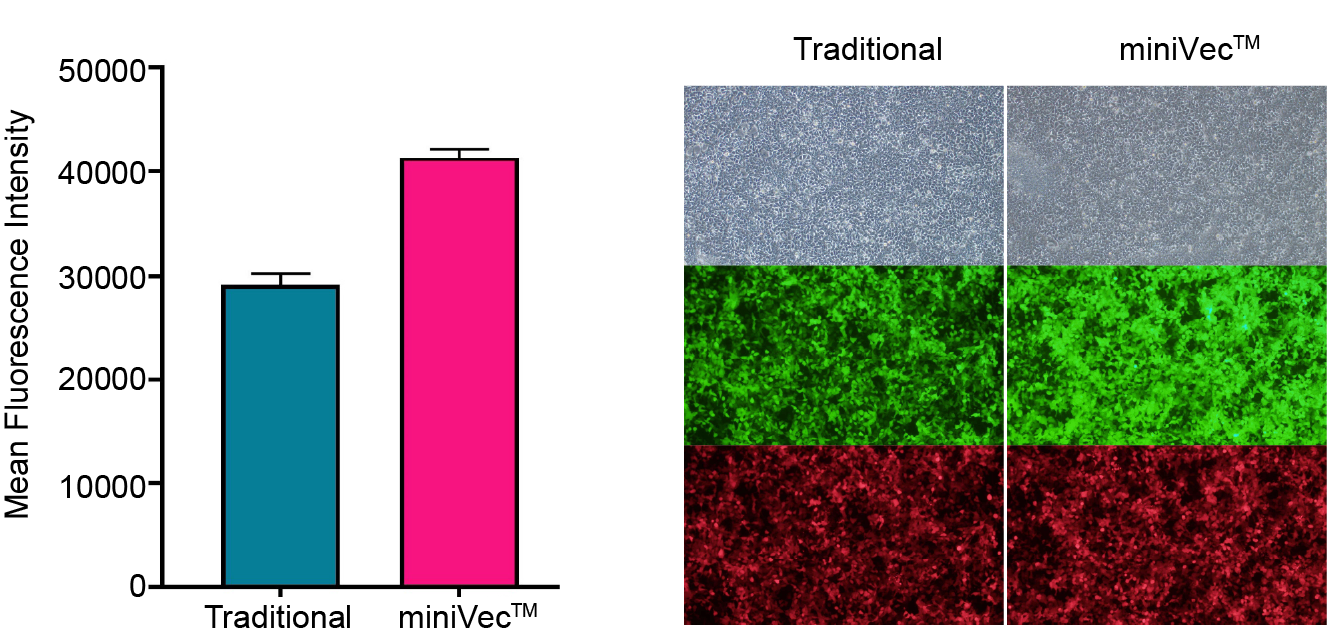
Figure 3. miniVec™ exhibits increased EGFP expression compared to traditional plasmids in HEK-293T cells 48 hours after equal molar transfection as measured by flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy. An mCherry expressing plasmid was co-transfected as the transfection control. Average mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of all viable cells was calculated.
miniVec™ plasmids are further validated for enhanced transgene expression in vivo compared to traditional plasmids. Due to these features, miniVec™ is an ideal candidate for gene therapies and DNA vaccines.
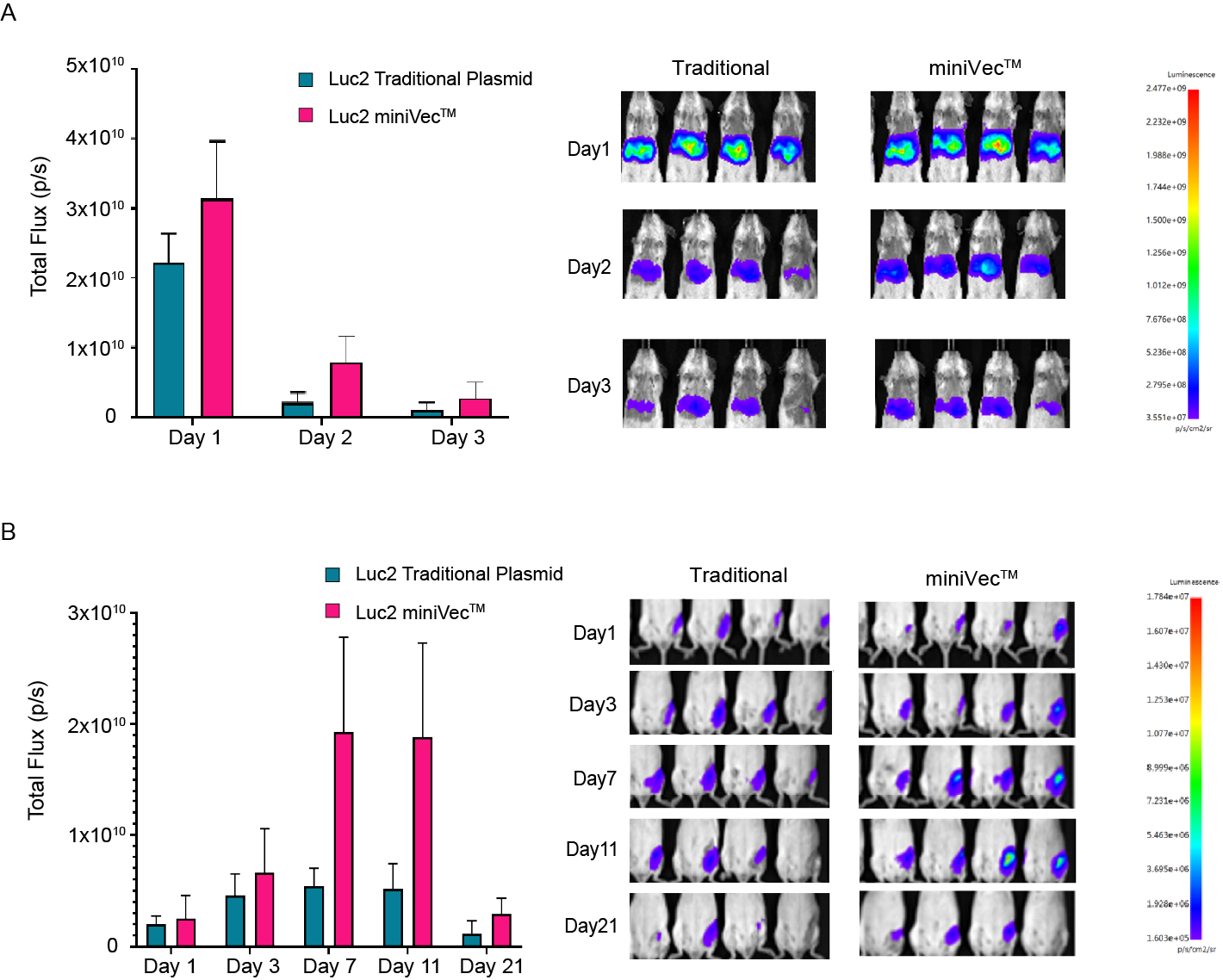
Figure 4. miniVec™ exhibits increased and prolonged luciferase expression compared to traditional plasmids in mice. Plasmids (CAG>Luc2) were administered (A) intravenously or (B) intramuscularly at equal molarity.
Efficient Transposon Delivery
miniVec™ is an ideal choice for piggyBac and Sleeping Beauty transposon systems due to its streamlined design, reduced metabolic burden on host cells, and enhanced safety profile. These features allow miniVec™ to achieve comparable or increased transposition efficiency in cells.
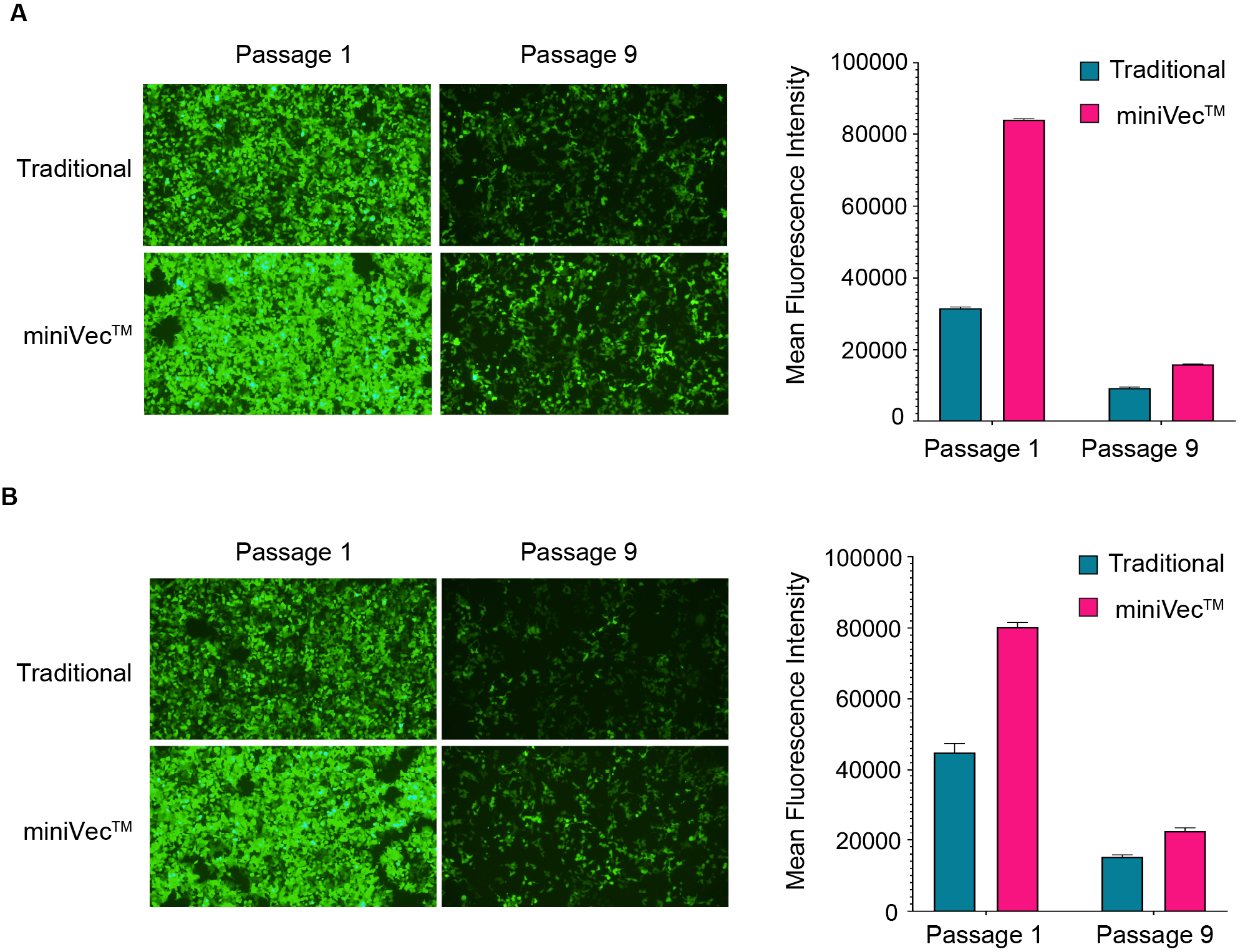
Figure 5. Comparative analysis of transposition efficiency between traditional and miniVec™ plasmids for (A) piggyBac and (B) Sleeping Beauty systems in HEK-293T cells as measured by flow cytometry. Average mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of all viable cells was calculated.
Safer Source Materials for Virus Packaging
miniVec™ plasmids offer a safer alternative to traditional antibiotic-dependent plasmids in the GMP production of recombinant viruses, reducing the risk of potential antibiotic residues in the final product and mitigating the risk of horizontal gene transfer. This enhances the safety profile of the GMP process, aids in compliance with regulatory standards, and ensures the purity of the final product. In addition, miniVec™ packaging plasmids have been shown to achieve higher titer for virus packaging than traditional plasmids.
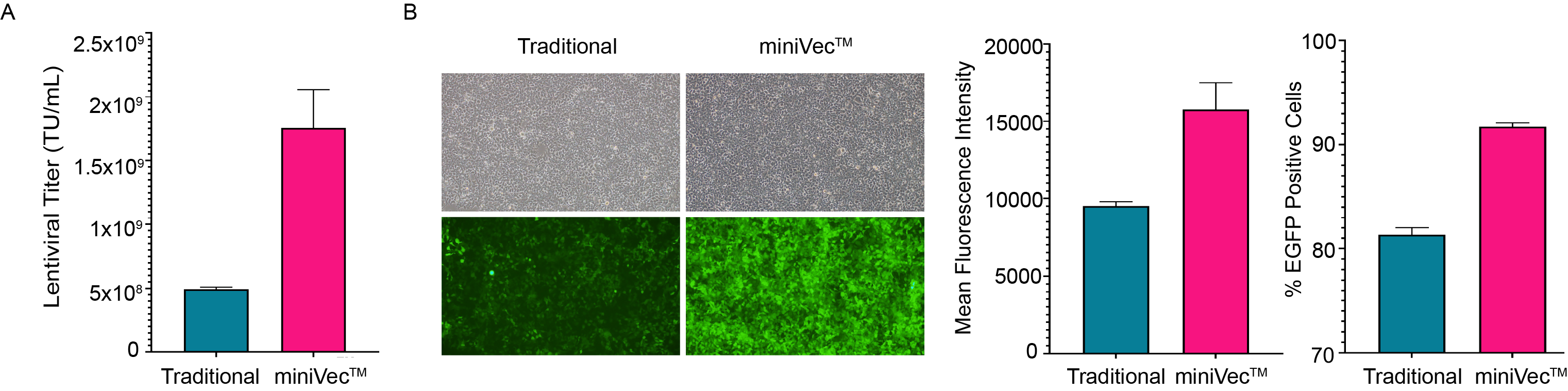
Figure 6. Comparison of lentivirus packaging using traditional and miniVec™ plasmids. (A) Higher lentivirus titer is achieved using miniVec™ plasmids. Functional viral titers were measured by qPCR post-transduction. (B) Comparison of EGFP expression through equal volume transduction of lentivirus in-parallel produced using traditional vs. miniVec™ plasmids. Average mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of all viable cells was calculated.




