IVT mRNA
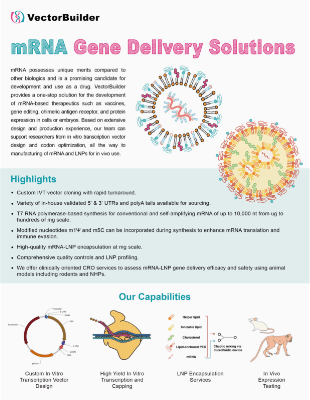
As a trendy genetic medicine, in vitro transcribed mRNA (IVT mRNA) has several advantages for gene delivery including no risk of insertional mutagenesis, streamlined cell-free manufacturing, and the ability to develop personalized treatments. IVT mRNA can be applied to a wide range of therapeutic applications including vaccines, protein replacement, CAR-T, and CRISPR gene editing. VectorBuilder's expert RNA team specializes in custom IVT mRNA design, production, and LNP encapsulation, with a wide range of customization possibilities.
Talk to Our Experts
Highlights

Royalty-free IVT backbone for mRNA production with no IP constraints for commercial use
As fast as 5 weeks from vector cloning
to LNP encapsulation
Comprehensive customization including capping methods, modified nucleotides, poly(A) tails, and UTRs

Expert design and production team specialized in optimizing your mRNA
for the highest expression, yields, and quality
Offering Details
- Premade mRNA products
- Therapeutic RNA Development: IVT vector design & cloning, IVT RNA production & purification.
- LNP Encapsulation: standard and custom formulations, antibody-conjugated LNP.
- CDMO Services: process development, GMP manufacturing, fill/finish.
Technical Information
The following diagram depicts the fundamental components of mRNA, and each component plays critical roles in regulating gene expression. There are a variety of methods for assembling these components in vitro and VectorBuilder can help assess the best method for achieving optimal expression, yields, and purity for your project. You can also read the Vector Academy article The Basics of mRNA Therapeutics for a more detailed overview of therapeutic mRNA.
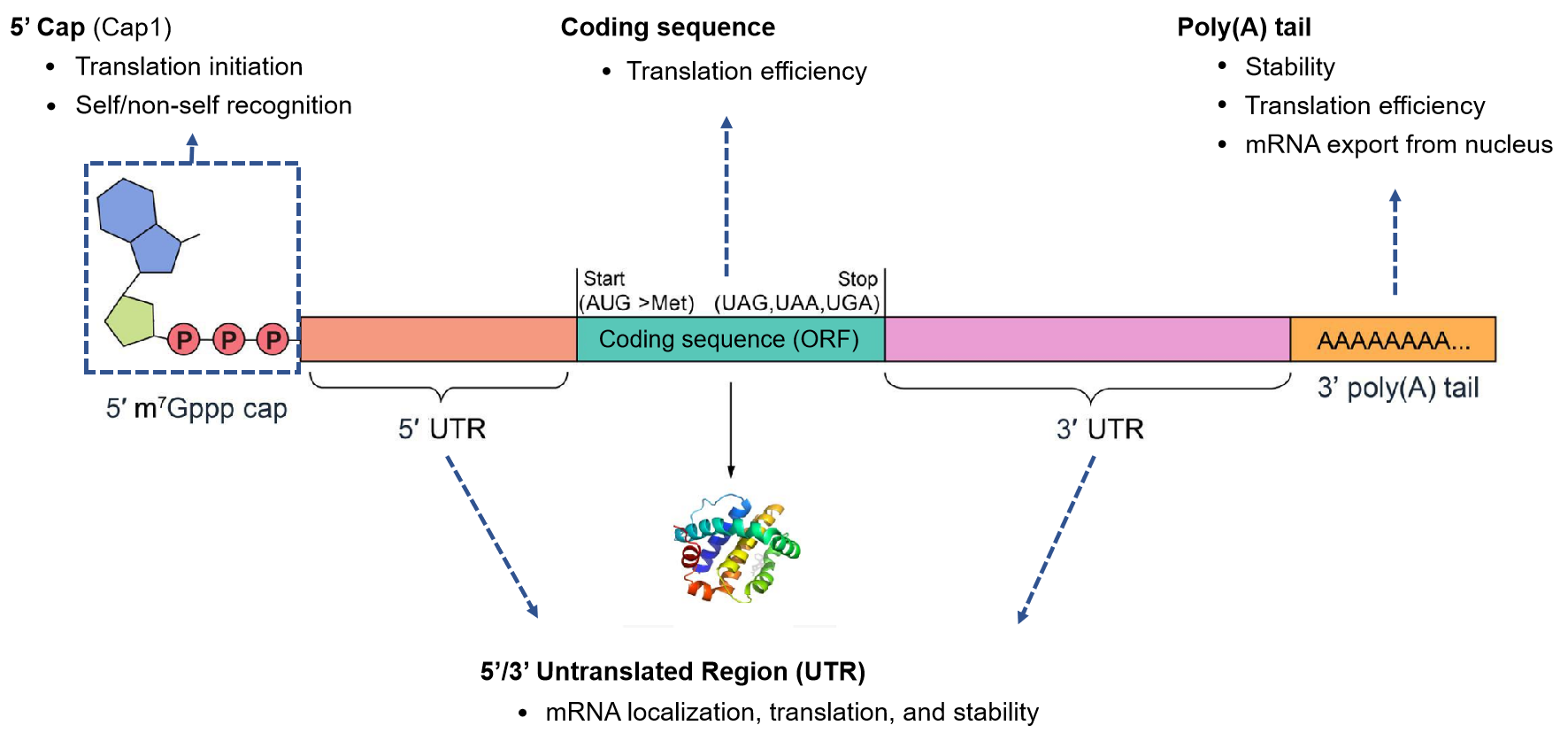
Figure 1. Structure and function of mRNA components.
- mRNA vaccine development
- CRISPR gene editing
- CAR-T
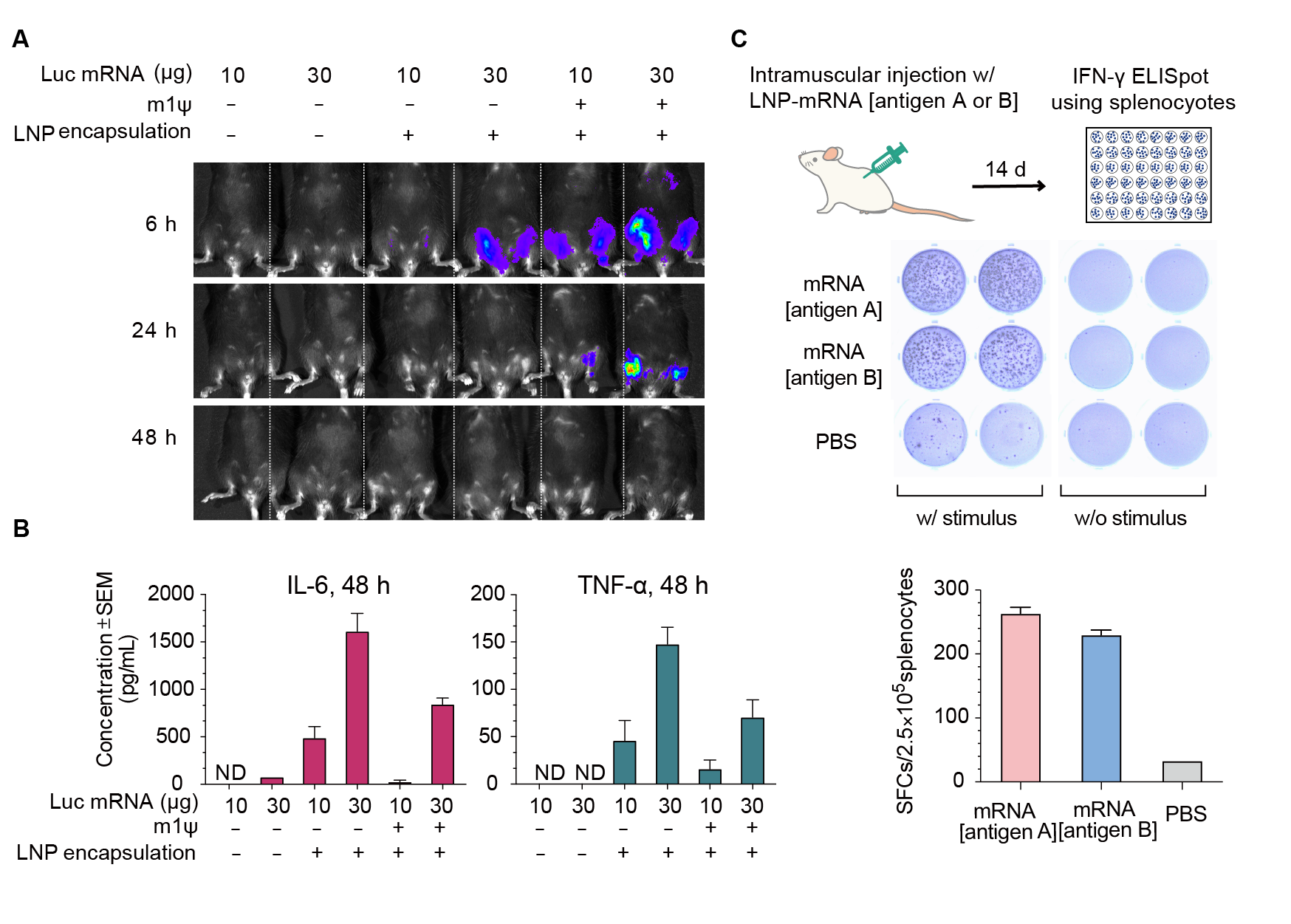
Figure 2. Expression of luciferase (Luc) mRNA and mRNA induced immune response in mice. (A) Luciferase activity visualized by live imaging at 6 h, 24 h, and 48 h post-injection. (B) Two pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-6 and TNF-⍺, were quantified in the serum at 48 h post-injection. Error bars represent standard errors. Mice strain: C57BL/6J; mice age: 8 weeks; injection method: intramuscular injection. (C) IFN-γ ELISpot assay of splenocytes derived from Balb/C mice 14 days post intramuscular injection of 30 ug LNP-encapsulated mRNA coding for viral antigen A, viral antigen B, or control PBS.
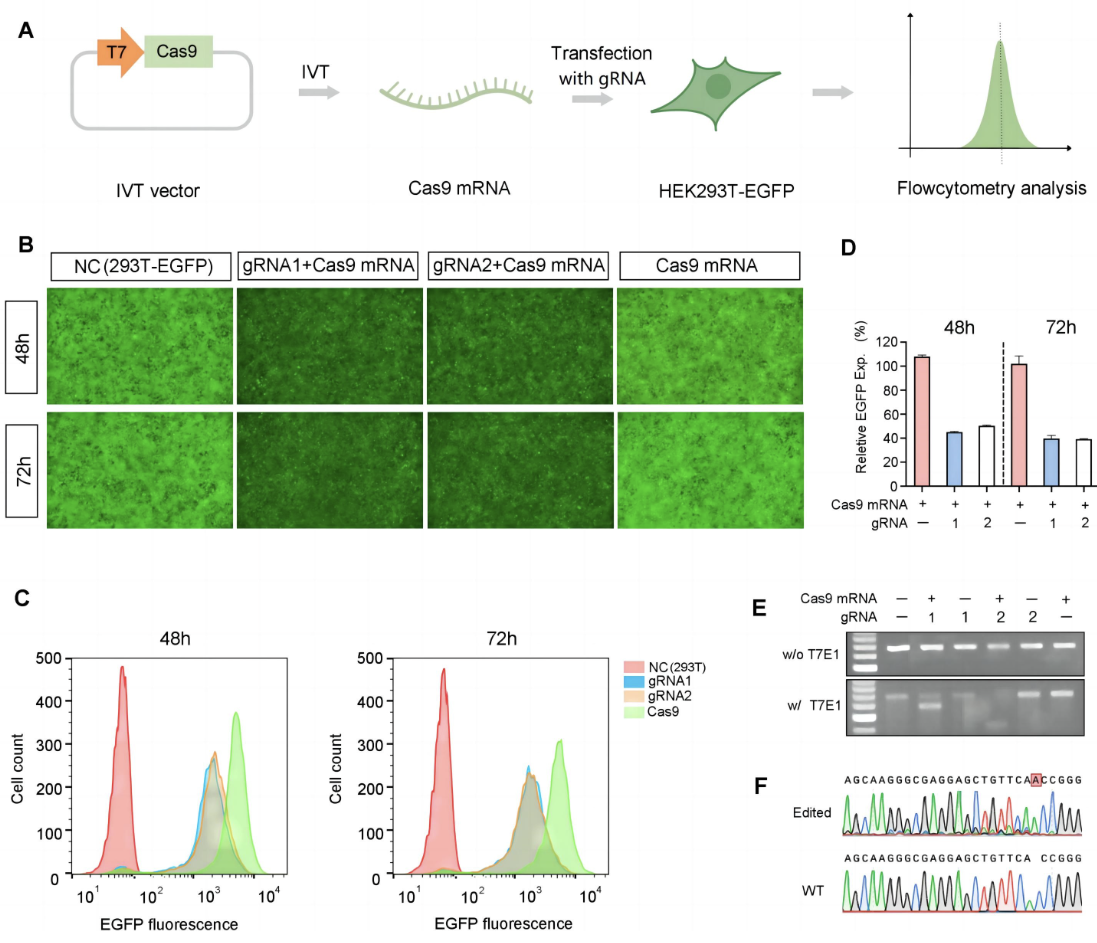
Figure 3. Validation of hSpCas9 mRNA in vitro. (A) IVT Cas9 mRNA was transfected into 293T-EGFP cells with two types of EGFP-targeting gRNA. EGFP expression in non-treated (NC) and transfected cells was observed by microscopy (B) and quantified using flow cytometry (C + D). (E + F) The editing to EGFP genes on the genome was further confirmed by T7E1 assay and Sanger sequencing.
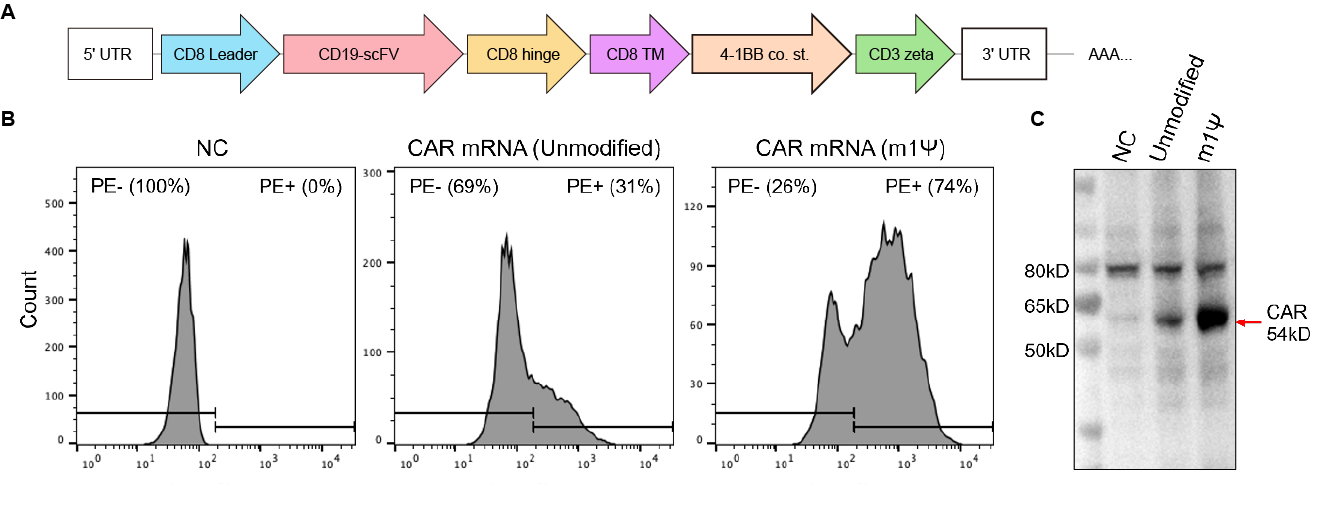
Figure 4. Validation of IVT Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) mRNA expression in 293T cells. (A) CD19 CAR mRNA with robust 5’/3’ UTRs and poly(A) was generated with or without N1-Methylpseudouridine (m1Ψ) and used to transfect 293T cells. (B) 24h post transfection, cells were incubated with PE-labeled human CD19 to quantify CAR expression using FACS. (C) The expression was further validated using an anti-CD3zeta antibody and western blot.
FAQ
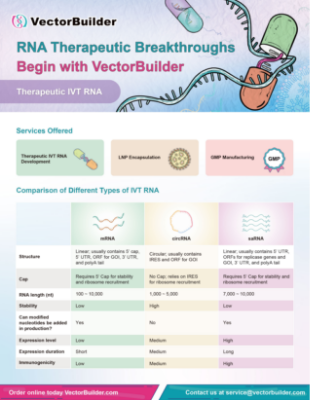
| mRNA | circRNA | saRNA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Linear; usually contains 5’ cap, 5’ UTR, ORF for GOI, 3’ UTR, and poly(A) tail | Circular; usually contains IRES and ORF for GOI | Linear; usually contains 5’ UTR, ORFs for replicase genes and GOI, 3’ UTR, and poly(A) tail |
| Cap | Requires 5' Cap for stability and ribosome recruitment | No Cap; relies on IRES for ribosome recruitment | Requires 5’ Cap for stability and ribosome recruitment |
| RNA length (nt) | 100 ~ 10,000 | 1000 ~ 5000 | 7000 ~ 10,000 |
| Stability | Low | High | Low |
| Can modified nucleotides be added in production? | Yes | No | Yes |
| Expression level | Low | Medium | High |
| Expression duration | Short | Medium | Long |
| Immunogenicity | Low | Medium | High |
Cap 0 refers to N7-methylguanosine (m7G) that is added to the 5’ end of eukaryotic mRNAs via a 5’ to 5’ triphosphate linkage. This modification is added via a series of enzymatic reactions that occur co-transcriptionally and functions to regulate nuclear export, transcript stability, and promotes translation of the mRNA through recognition by eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF4E). Cap 1 refers to the addition of a methyl group to the 2’O on the first nucleotide (m7GpppNm) of the transcribed mRNA sequence in addition to the m7G cap. In mammalian cells, cap 1 structure is an important marker for mRNA to be recognized as self and not targeted by innate immunity. Adding cap 1 structure to synthesized mRNA has been demonstrated to enhance mRNA expression in vivo and reduced its immunogenicity.
Capping for in vitro transcribed RNA can occur either co-transcriptionally with cap analogs or post-transcriptionally via enzymatic reactions. We offer both capping methods, and the efficiency of them has been well validated using LC-MS. Depending on the client-preferred capping method, we will choose a compatible backbone for cloning the IVT mRNA vector from the beginning.
Cells contain cytosolic and endosomal RNA receptors that activate the immune response upon recognition of foreign RNA. Modified nucleotides are commonly found in endogenous cellular RNA. Incorporating certain modified nucleotides in IVT mRNA reduces its immunogenicity, alters secondary structure, and increases translation efficiency and half-life in a sequence-dependent manner. We provide a wide range of modified nucleotides, including the commonly used N1-Methylpseudouridine (m1Ψ) and 5-Methylcytosine (m5C). N1-Methylpsuedouridine and 5-Methylcytosine are naturally occurring nucleotides that were first identified in tRNAs, however, their use in coding mRNAs has only recently been appreciated. These methylated derivatives of uridine and cytosine can replace their canonical nucleotides in mRNA IVT and translation without altering traditional Watson-Crick base pairing. A major advantage to their use in mRNA therapeutics is their ability to alter recognition by RNA immune receptors thus mitigating unwanted immune effects and enhancing transcript stability and translation.
Documents
Brochures & Flyers User InstructionsCertificate of Analysis (COA)
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)